This article originally appeared in Business Insurance.
In case you missed it, October was Cybersecurity Awareness Month. Promoting awareness is generally good, but when it comes to cyber risk, a month on the calendar seems inadequate. Cybersecurity awareness — and even more importantly, action — should be an everyday thing for all organizations.
As we can see by even a casual reading of news headlines, cyber is a constantly evolving risk, and cyber criminals continue to exploit systems to perpetrate attacks. Improving cybersecurity and cyber risk management are not do-it-yourself tasks. Securing your organization and its system users, and mitigating loss, require expert advice. Do your insurance company partners have that expertise in-house?
Right now, the market for cyber insurance is highly competitive. Coverage has become widely available, accompanied by varying services, and standards are few. These factors tend to obscure differences in cyber insurance providers. Whenever new market entrants compete for customers, prices tend to fall, and that is also happening in cyber insurance.
The problem with this trend is it’s not sustainable. Cyber risk underwriters should closely align rates, terms and conditions with the customer’s exposures, and offer effective ways to mitigate that risk. The goal of any cyber risk management program should be to prevent loss, mitigate the impact of cyber events, and be a means of achieving resiliency. Appropriate incentives for risk mitigation can help keep the cyber insurance market stable and able to evolve to respond to new and emerging cyber threats.
Risk Controls: Basic and Advanced
The dynamic nature of cyber risk means that policyholders need ongoing risk management. There are some similarities between cyber and property insurance. One is in how risk controls are applied. Property risk engineering is a proven way to fortify structures against natural and human-caused perils, and to improve resilience. If you’ve ever seen aerial photographs of buildings after a natural disaster such as a hurricane, you might notice that some structures remain intact while others are heavily damaged. Properties that utilize risk engineering fare much better and recover more quickly than those that don’t. Cyber risk is quite similar in this regard.
When sound underwriting is paired with risk controls, policyholders are in a far better position to cope with their risks and to recover faster when losses do occur. Arch Insurance’s cyber risk engineering team has identified eight critical controls that offer basic risk management (see graph):
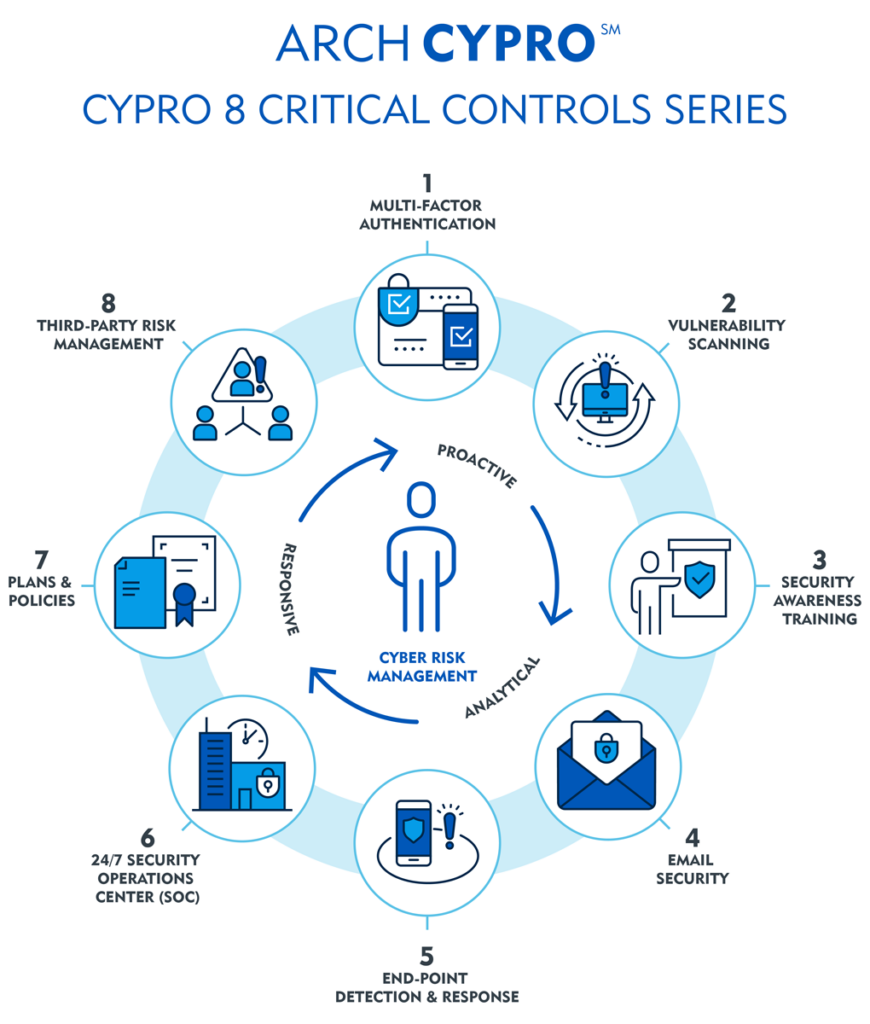
- Multi-factor authentication. MFA can block unauthorized users by requiring more than one means of digital identification to gain access to an organization’s systems.
- Vulnerability scan. This patrols an organization’s systems for potential weaknesses, not unlike a security guard walking the perimeter of a building.
- Security awareness training. Informing and educating the workforce helps organizations promote a culture of cybersecurity.
- Email security. Phishing remains a widely used means of delivering malware, so an email security control applies advanced filtering, detection and neutralization of malicious emails.
- End-point detection and response. This system monitors each device connected to an organization’s network, detects threats and takes action to neutralize them.
- 24/7 security operations center. A round-the-clock radar for cyber threats and anomalies that could signal nefarious activity, this control ensures swift detection and response.
- Plans and policies. These are an organization’s cyber playbook, laying out procedures to follow during a crisis.
- Third-party risk management. An extension of the cybersecurity chain, this control helps organizations ensure that partners and vendors meet security standards so they are not weak links.
Advanced risk controls go beyond the basic ones described above and position organizations to have a strong cyber risk management culture. These additional controls also foster collaboration between the cybersecurity and risk management teams, resulting in a well-orchestrated, robust solution to combat cyber threats.
Arch’s Approach to Cyber Risk
At Arch Insurance, we believe cyber insurance should be about more than issuing payment. By combining a cyber insurance policy with risk engineering advisory services, Arch aims to strengthen policyholders, making them better risks, and helping to improve their businesses.
To achieve this goal, we have cyber experience and expertise available in-house. Our Arch Cyber Risk Engineering (ACRE) team advises policyholders about their exposures and recommends controls they can implement to mitigate their risks. Arch underwriters also have a deep understanding of security and risk transfer needs, and we’re dedicated problem-solvers. Finally, Arch enlists expert partners to provide comprehensive support services to help policyholders respond to cyber incidents.